ServiceX¶
The High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider (HL-LHC) faces enormous computational challenges in the 2020s. The HL-LHC will produce exabytes of data each year, with increasingly complex event structure due to high pileup conditions. The ATLAS and CMS experiments will record ~ 10 times as much data from ~ 100 times as many collisions as were used to discover the Higgs boson.
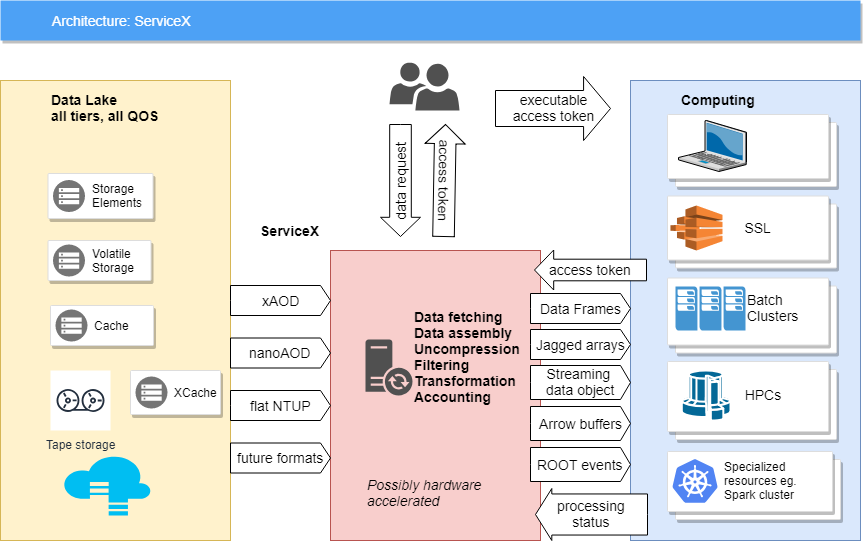
ServiceX is a scalable data extraction, transformation and delivery system deployed in a Kubernetes cluster designed to efficiently extract columnar data from large datasets.
Concepts¶
This section describes the concepts that are important to understand when working with ServiceX.
Datasets¶
Datasets are groups of experimental data from which columnar data can be extracted. ServiceX supports four sources of data:
Rucio
CERN Open Data Portal
List of File accessible via HTTP or XRootD
EOS Directory
Queries¶
Queries are used to extract data from a dataset. They specify the columns to extract, the events to include in the output. There are several types of queries supported by ServiceX:
func-adl
Python Function
Dictionary of uproot selections
Sample¶
A sample is a request to extract columnar data from a specified dataset, using a specific query. It results in a set of output files containing the requested data that can be used in an analysis via awkward, RDF, etc..
Transformation Request¶
Multiple samples can be submitted to ServiceX at the same time. Each sample is processed independently, and the results can be retrieved as files downloaded to a local directory or directly accessed via a URL from ServiceX’s output cache.
Local Cache¶
ServiceX maintains a local cache of the performed queries and their results. This cache can be used to avoid re-running queries that have already been executed.